According to the Small Business Administration (SBA), 20% of small businesses fail in the first year, 50% after 5 years and only 33% make it up to 10 years and more, primarily based on their BEP performance.
During an enterprise’s earlier stages, founders understand the importance of a “break-even point”, with the crucial question, “When will I break even?”.
So what is a break-even point? The BEP aims to define the number of sales needed to cover costs, ensuring the company’s safety margin.
“On average, it takes 2 to 3 years for a company to reach its break-even point.”
Successful business leaders know that calculating their break-even point is crucial for any business plan, as it is effectively an enterprise’s “make or break” formula. Essentially, breaking even is a healthy sign of growth. For this reason, reducing business-specific risks whilst selling a product or service at a price that meets market levels is a company’s true foundation.
This article explains everything you need to know about BEP: what break-even means, the break-even formula, and how to use break-even analysis to secure your business’s future.
Index
What is a break-even point (BEP)?
The break-even point plays a significant role in determining if your product or service is worth selling. When total cost and revenue are equal, there is no loss or gain in your business. This is determined through a break-even analysis.
If an enterprise has reached its break-even point, it is operating at neither a net loss nor net gain. Beyond this point, additional income contributes to extra profits for the business.
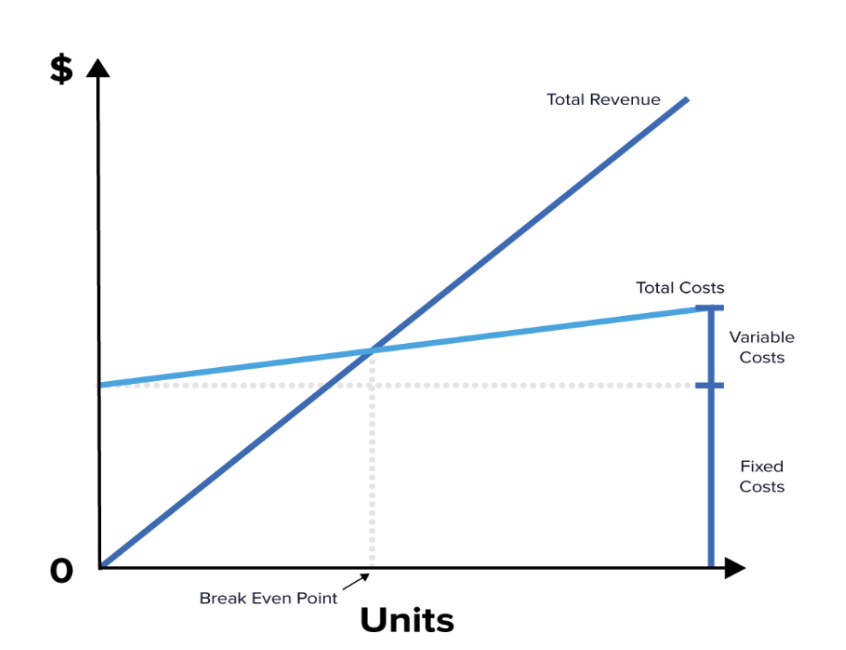
Once you have determined your BEP number, you can analyse your costs from rent, labour and materials and define your price structure through three fundamental questions:
1 – Are your prices too low or your costs too high to reach your BEP?
2 – When will you foresee your break-even point?
3 – Does my business achieve sustainable results?
At this point, you will be able to determine whether your business model is in good form or whether you need to rethink your costs and/or your business model.
Don’t mistake accounting break-even points vs financial break-even points
There are a few differences between accounting and financial break-even points – let’s start by defining the two terms:
- The accounting break-even point is the easiest and standard way to analyse your profit. You can easily calculate the BEP by calculating the number of units that should be sold to cover your company’s total expenses (materials, production, salaries, rent).
- The financial break-even point is more complex as it measures the company’s earnings and not the product or number of units sold. Notably, a financial break-even point is the number of earnings before interest and taxes, resulting in zero net income or zero earnings per share.
Understanding breakeven points (BEPs) and their role in your success
Performing a break-even analysis is required in any business to set marketable prices. Through the BEP, you will establish clear sales targets whilst identifying weaknesses (i.e. sales and marketing strategy).
When understanding the work required to break even, a company can set significant revenue targets while perfecting its business strategy.
“The break-even theory is based on the fact that there is a minimum production level at which a venture neither make profit nor loss.”
M. B. Ndaliman
4 Factors that increase a company’s break-even point
As you calculate a company’s breakeven point on variables, the BEP may increase or decrease depending on three main factors:
1 – Increase in production costs
It is probable that whilst customer demand remains the same, the price of variable costs increases – such as the price of raw materials, an increase in salaries, higher utility rates or a rent increase. Businesses are at the mercy of these price fluctuations, leading to a higher BEP.
2 – Increase in customer sales
An increase in customer demand leads to higher sales; the company has to produce more to meet the higher demand, thus raising the break-even point to cover additional costs.
3 – Equipment repair
Unfortunately, mishaps happen, and unpredictable breaks or malfunctions can occur. Repair costs need to be considered whilst the target numbers are not completed in the given time frame. In this case, equipment failures result in higher operating costs and a higher return on investment.
4 – Break-even decrease
A company can successfully get to a break-even decrease when it increases its product contribution margin, which then decreases the product’s associated costs and expenses, thus expanding the amount of revenue each product generates.
Next step: Understanding options trade breakeven points
To understand the full scope and importance of a break-even point, it is helpful to understand the areas in which it is of importance.
In options trading, the break-even price is the price in the asset at which investors can choose to exercise or dispose of the contract without incurring a loss.
So, what is an option?
An option refers to a financial tool based on the value of underlying stakes such as stocks. An options contract allows the buyer to purchase or sell the asset depending on the type of contract. The holder does not have to buy or sell the investment if they decide against it.
How to calculate your break-even point?
A break-even point equation is ultimately a financial calculation used to determine the number of products or services you need to sell to cover your production costs.
There are two simple break-even formulas:
1) The number of units your business has sold
2) The points in sales dollars.
- Break-Even Point in Units
For this equation, divide the fixed costs by the unit revenue minus the variable cost per unit.
Break-Even Point (Units) = Fixed Costs ÷ (Revenue per Unit – Variable Cost per Unit)
- Break-Even Point In Sales Currency
Firstly determine your contribution margin: subtract the variable costs from the price of a product.
Contribution Margin = Price of Product – Variable Costs
Then divide the fixed costs by the contribution margin:
Break-Even Point (sales dollars) = Fixed Costs ÷ Contribution Margin
In simpler words:
- Fixed costs: Costs that do not change (salary, rent, building machinery).
- Sales price per unit or revenue: The selling price per unit.
- Variable cost per unit: The variable costs sustained to create a unit (materials, labour).
- Break-even point: Once sales match your fixed and variable costs and your business reports net earnings of $0 – sales above that point contribute to your net profit.
Break-even point calculation example
Simply Business has fixed costs (lease, salaries, taxes) equal to $60,000. Their product is a gadget. Their variable costs to produce the gadget (raw material, factory labour, sales commissions) are $0.80 per unit. The gadget is sold at $2.00 each.
With this information and using the following break-even point equation, we can calculate the BEP for Simply Business’ gadget:
$60,000 ÷ ($2.00 – $0.80) = 50,000 units
What does this mean?
Simply Business has to produce and sell 50,000 gadgets to cover its total expenses (fixed and variable). With these sales, they will not make any profit but only break even.
How to reduce the break-even point
A company’s break-even point must be kept as low as possible to maintain the company’s profitability even when sales decline. There are four ways to do so:
-
Reduce fixed costs
The average company has several fixed costs, such as rent payments, employee salaries, and production equipment. By lowering these costs, the business needs fewer sales to cover the remaining fixed costs.
-
Reduce variable costs
You can raise the average contribution margin earned on each sale to decrease your BEP. This can be done by reducing variable costs by rethinking the products, standardising the product across platforms and allowing volume purchase discounts, or by increasing product quality, thus lessening guarantee repairs.
-
Raise product prices
Another way to reduce your company’s BEP is to set higher prices. This method only works if buyers are not particularly sensitive to price, i.e. when the business is established as a high-quality provider. This approach can be risky as your customers could go elsewhere if this strategy is not correctly implemented.
-
Go for outsourcing
Profitability may increase when a business chooses to outsource. This can result in lower manufacturing costs as production volume increases.
How to use break-even analysis in aim to decrease your BEP
As this article explains, one very effective way to reduce your risk is to conduct a break-even analysis. This BEP analysis will advise how to break even and regain your original investment. It is not only beneficial for a starting business but should be used for daily operations.
For starting a business
Starting your own business without a break-even analysis is a recipe for disaster. Calculating your BEP will help decide if your business plan is achievable whilst helping break down and examine company costs and give you clear visibility on your pricing strategy.
Prices
If your BEP shows that your current price is too low to break even within your desired timeframe, you should consider increasing the product’s cost. However, check the cost of comparable items as you don’t want your consumers to buy from competitors.
Materials
Choosing the suitable raw material is crucial, as you need both quality and sustainable costs. Thorough research and negotiation are key to the process.
New products
Before launching a new product, consider both the new variable and fixed costs, such as design and promotion fees.
Planning
Setting longer-term goals is easier when you know exactly how much you need to make. For example, if you want to move to a larger warehouse, you can determine the amount you need to sell to cover your higher rent.
Goals
Knowing how many units you need to sell or how much money you need to make to break even can act as a strong motivational tool for you and your team.
In summary
Ensuring your business has the right break-even point is crucial for any financial assessment, and the good news is that there is a simple mathematical equation to get there.
Nonetheless, the break-even point should be calculated accurately and consider the overall company finances.
An enterprise can implement two simple steps to optimise its break-even point by 1) reducing fixed and variable costs, 2) raising product prices and/or outsourcing its raw materials. Consequently, these actions will depend on the circumstances of both the business and the market.
With this knowledge, a business can correct its approach to improving profitability whilst preparing the necessary steps to reach its business goals.
To find out how to simply your business accounting, learn more about SimplyPayMe’s automated software.